Configure-dkim,spf,dmarc-to-protect-against-spoofing: Difference between revisions
(Created page with " <big>Email Authentications prevent the email from going into the spam folder of recipients. cPanel uses DKIM and SPF to reduce the amount of spam mails. Enabling these features will prevent spammers from forging messages that claims to be coming from your domain.</big> <big>DKIM</big> <big>Domain Key Identification Mechanism (DKIM) verifies your incoming emails to check whether they are same as they were before when they were sent. This means, if they are altered duri...") |
No edit summary |
||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
<big> | <big>'''Email authentication:''' Email authentication makes sure your emails '''don’t land in the recipient’s spam folder'''.</big> | ||
<big> | <big>In '''cPanel''', three methods are used: '''DKIM, SPF, and DMARC'''.</big> | ||
<big> | <big>These features protect your domain and stop spammers from sending fake emails using your name.</big> | ||
---- | |||
<big>Enabling DKIM</big> | === <big>DKIM (Domain Keys Identified Mail)</big> === | ||
* <big>DKIM checks if an email is '''safe and unchanged''' during delivery.</big> | |||
* <big>It also verifies that the email really came from the sender’s address.</big> | |||
* <big>This helps reduce fake or spam emails.</big> | |||
<big>'''How DKIM Works:'''</big> | |||
# <big>When you send an email, it is signed with a '''digital signature''' using a private key.</big> | |||
# <big>When the receiver gets the email, their system checks it using your '''public key'''.</big> | |||
# <big>If the signature matches → the email is valid.</big> | |||
# <big>If the signature does not match → the email is treated as '''spam'''.</big> | |||
---- | |||
=== <big>Enabling DKIM in cPanel</big> === | |||
<big>You just need to go to '''cPanel → Email Authentication''' and turn on '''DKIM'''.</big> | |||
<big>Once enabled, all outgoing emails from your domain will automatically include this security signature.</big> | |||
<big>To enable DKIM follow these steps −</big> | <big>To enable DKIM follow these steps −</big> | ||
| Line 60: | Line 78: | ||
<big>'''Step 2''' − Find SPF setting, if enabled, then click '''Disable''' button to disable SPF.</big> | <big>'''Step 2''' − Find SPF setting, if enabled, then click '''Disable''' button to disable SPF.</big> | ||
=== <big>DMARC (Domain-based Message Authentication, Reporting, and Conformance)</big> === | |||
<big>DMARC works together with '''SPF''' and '''DKIM''' to stop fake emails. It tells mail servers what to do if an email fails authentication and also sends reports back to the domain owner.</big> | |||
<big>DMARC | |||
''' | |||
=== <big>How DMARC Works</big> === | |||
* <big> | # <big>Domain owner adds a '''DMARC record''' in DNS.</big> | ||
* <big> | # <big>When an email arrives:</big> | ||
* <big> | #* <big>Server checks '''SPF''' and '''DKIM'''.</big> | ||
* <big> | #* <big>It also checks if the email matches the sender’s domain.</big> | ||
# <big>Based on the DMARC policy → action is taken:</big> | |||
#* <big>'''none''' → Just monitor, no action.</big> | |||
#* <big>'''quarantine''' → Put in spam/junk.</big> | |||
#* <big>'''reject''' → Block the email.</big> | |||
# <big>Reports are sent to the email address in the DMARC record.</big> | |||
=== <big>DMARC Policies</big> === | |||
* <big> | * <big>'''p=none''' → Only monitoring, no blocking.</big> | ||
* <big> | * <big>'''p=quarantine''' → Suspicious emails go to spam.</big> | ||
* <big> | * <big>'''p=reject''' → Block fake emails completely.</big> | ||
=== <big>Steps to Implement DMARC</big> === | |||
# <big>'''Plan''' → List all sources sending emails for your domain.</big> | |||
# <big>'''Add SPF''' → Publish SPF record in DNS with allowed servers.</big> | |||
# <big>'''Add DKIM''' → Generate keys, sign emails, and publish public key in DNS.</big> | |||
# <big>'''Enable DMARC (p=none)''' → Collect reports first, no blocking.</big> | |||
# <big>'''Fix Issues with Third Parties''' → Make sure they pass SPF/DKIM.</big> | |||
# <big>'''Increase Enforcement''' → Change policy to quarantine → then reject.</big> | |||
# <big>'''Full Protection''' → Set policy to reject once everything works fine.</big> | |||
<big>'''Example Records:'''</big> | |||
* <big>SPF: <code>v=spf1 ip4:192.0.2.0/24 include:_spf.example.com -all</code></big> | |||
* <big>DMARC (monitoring): <code>v=DMARC1; p=none; rua=<nowiki>mailto:dmarc-reports@example.com</nowiki></code></big> | |||
* <big>DMARC (reject): <code>v=DMARC1; p=reject; rua=<nowiki>mailto:dmarc-reports@example.com</nowiki></code></big> | |||
* | * | ||
Revision as of 05:17, 6 September 2025
Email authentication: Email authentication makes sure your emails don’t land in the recipient’s spam folder.
In cPanel, three methods are used: DKIM, SPF, and DMARC.
These features protect your domain and stop spammers from sending fake emails using your name.
DKIM (Domain Keys Identified Mail)
- DKIM checks if an email is safe and unchanged during delivery.
- It also verifies that the email really came from the sender’s address.
- This helps reduce fake or spam emails.
How DKIM Works:
- When you send an email, it is signed with a digital signature using a private key.
- When the receiver gets the email, their system checks it using your public key.
- If the signature matches → the email is valid.
- If the signature does not match → the email is treated as spam.
Enabling DKIM in cPanel
You just need to go to cPanel → Email Authentication and turn on DKIM.
Once enabled, all outgoing emails from your domain will automatically include this security signature.
To enable DKIM follow these steps −
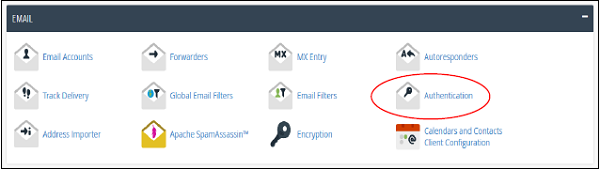
Step 1 − Open Email Authentication by clicking Authentication found under Mail Section of cPanel Home.
Step 2 − Find DKIM settings, if disabled then, click Enable button to Enable DKIM.
Disable DKIM
To disable DKIM follow these steps −
Step 1 − Open Email Authentication by clicking Authentication found under Mail Section of cPanel Home.
Step 2 − Find DKIM setting, if enabled, then click Disable button to Disable DKIM.
Note − To Enable DKIM, your Nameservers must point to your hosting. It is recommended that you use DKIM Authentication in your hosting.
Advertisement
SPF
Sender Policy Framework (SPF) helps in preventing outgoing messages to spams. This helps to prevent spammers in creating a message that looks like it is originated through your domain. SPF uses TXT type DNS resource records, which specify the hosts that send emails through your domain.
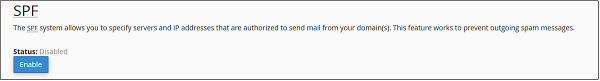
Enable SPF
To enable SPF, follow these steps −
Step 1 − Open Email Authentication by clicking Authentication found under Mail Section of cPanel Home.
Step 2 − Find SPF setting, if disabled, then click Enable button to Enable SPF.
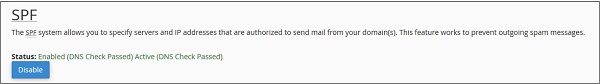
Disable SPF
To disable SPF, follow these steps −
Step 1 − Open Email Authentication by clicking Authentication found under Mail Section of cPanel Home.
Step 2 − Find SPF setting, if enabled, then click Disable button to disable SPF.
DMARC (Domain-based Message Authentication, Reporting, and Conformance)
DMARC works together with SPF and DKIM to stop fake emails. It tells mail servers what to do if an email fails authentication and also sends reports back to the domain owner.
How DMARC Works
- Domain owner adds a DMARC record in DNS.
- When an email arrives:
- Server checks SPF and DKIM.
- It also checks if the email matches the sender’s domain.
- Based on the DMARC policy → action is taken:
- none → Just monitor, no action.
- quarantine → Put in spam/junk.
- reject → Block the email.
- Reports are sent to the email address in the DMARC record.
DMARC Policies
- p=none → Only monitoring, no blocking.
- p=quarantine → Suspicious emails go to spam.
- p=reject → Block fake emails completely.
Steps to Implement DMARC
- Plan → List all sources sending emails for your domain.
- Add SPF → Publish SPF record in DNS with allowed servers.
- Add DKIM → Generate keys, sign emails, and publish public key in DNS.
- Enable DMARC (p=none) → Collect reports first, no blocking.
- Fix Issues with Third Parties → Make sure they pass SPF/DKIM.
- Increase Enforcement → Change policy to quarantine → then reject.
- Full Protection → Set policy to reject once everything works fine.
Example Records:
- SPF:
v=spf1 ip4:192.0.2.0/24 include:_spf.example.com -all - DMARC (monitoring):
v=DMARC1; p=none; rua=mailto:dmarc-reports@example.com - DMARC (reject):
v=DMARC1; p=reject; rua=mailto:dmarc-reports@example.com